Figure 1
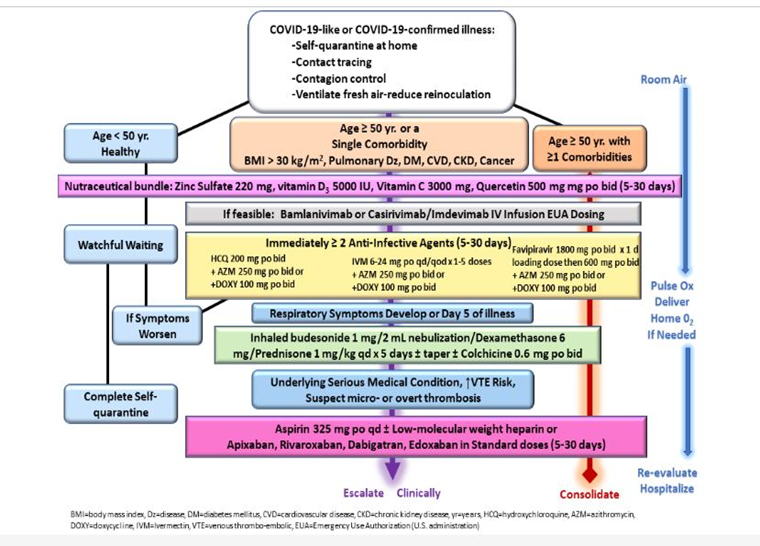
2. Sequential multidrug treatment algorithm for ambulatory acute COVID-19 like and confirmed COVID-19 illness in patients in self-quarantine. Yr = year, BMI = body mass index, Dz = disease, DM = diabetes mellitus, CVD = cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, HCQ = hydroxychloroquine, IVM = ivermectin, Mgt = management, Ox = oximetry, reproduced with permission from reference.
Figure 2
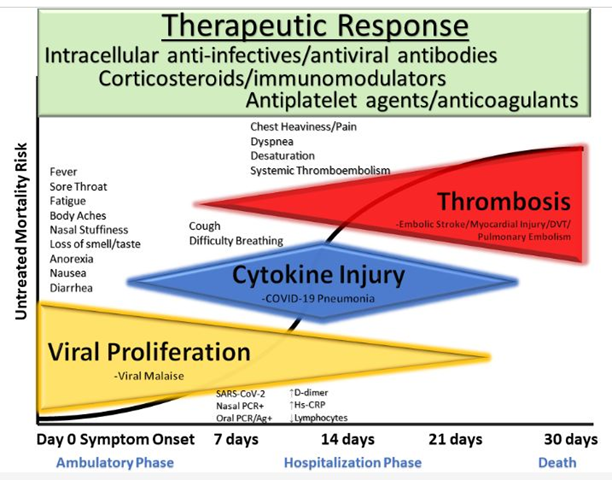
For the ambulatory patient with recognized signs and symptoms of COVID-19 on the first day (Fig. 1), often with nasal real-time reverse transcription or oral antigen testing not yet performed, the following three therapeutic principles apply (CDC Prevention, 2020):
- combination anti-infective therapy to attenuate viral replication
- corticosteroids to modulate cytokine storm
- antiplatelet agent/antithrombotic therapy to prevent and manage micro- or overt vascular thrombosis.
ADJUNCTIVE NUTRACEUTICALS
There has been considerable interest and study of the use of micronutrients and supplements for COVID-19 prophylaxis and treatment in combination with anti-infectives as first proposed by Zelenko and colleagues (Derwand et al, 2020) The aim of supplementation is to replenish those with deficiencies associated with COVID-19 mortality, and to aid in reducing viral replication and tissue damage.
- ZINC alone is a potent inhibitor of viral replication; and in combination with hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is potentially synergistic in reducing viral replication since HCQ is a zinc ionophore facilitating intracellular entry and inhibition of intracellular viral replication. This readily available nutrient could be deployed at the first signs of COVID-Zinc sulfate 220 mg (50 mg elemental zinc) can be taken orally per day
- VITAMIN D3 deficiency has been associated with increased COVID-19 mortality and is commonly confounded by increasing age, obesity, diabetes, darker skin tones, and lack of fitness. The suggested dose is 5000 IU of vitamin D3 per day. Up to 50,000 IU may be taken daily for 7 days in the event of a full blown Covid episode.
- VITAMIN C has been used in a variety of viral infections and could be useful in combination with other supplements in COVID-19. Multiple randomized trials of vitamin C given intravenously or orally are in progress at the time of this writing. A reasonable dose would be vitamin C 3000 mg per day minimum, and up to 10,000 mg. per day
- QUERCETIN is a polyphenol that has a theoretical mechanism of action that could reduce the activity of a SARS-CoV-2 entry through the ACE2 receptor, inhibit viral proteases via conveyance of zinc, and attenuate inflammatory responses mediated through interleukin-6. The mechanisms of action favorably affect viral replication and immune response, so it is conceivable that this agent taken in combination with others discussed could play an assistive role in reducing early viral amplification and tissue damage. The suggested dose of quercetin is 250 mg twice per day for preventive care; and 500 mg twice a day for confirmed active Covid..
- MELATONIN is an effective antioxidant that shows promising results in assisting the overall treatment of Covid. Achieving restorative sleep is critical to the Covid patient, and Melatonin accomplishes that, as well. It has been associated with shorter hospital duration and lessening malaise overall. As prevention, take 3-5 mg before bed.
Dr. Vladimir Zelenko (an associate of the FLCCC group) COVID PROTOCOL:
Moderate / High risk patients
Elemental Zinc 50-100mg once a day for 7 days Vitamin C 5000mg 1 time a day for 7 days Vitamin D3 10,000iu once a day for 7 days or 50,000iu once a day for 1-2 days Azithromycin 500mg 1 time a day for 5 days or Doxycycline 100mg 2 times a day for 7 days
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) 200mg 2 times a day for 5-7 days and/or Ivermectin 0.4-0.5mg/kg/day for 5-7 days Either or both HCQ and IVM can be used, and if one only, the second agent may be added after about 2 days of treatment if obvious recovery has not yet been observed etc.
IVERMECTIN
Ivermectin (IVM) is a broad spectrum anti-parasitic agent that has been shown to have anti-viral activity against a range of viruses including recently, SARS-CoV-2. With a proven safety profile with over 3.7 billion treatments, Ivermectin has been used alone or combined with either doxycycline or azithromycin in early clinical studies of patients with COVID-19.
it is reasonable in patients where HCQ cannot be used, that IVM (200-600 mcg/kg [6-36 mg] single oral dose given daily or every other day for 2-3 administrations) could be the base of SMDT intended to reduce viral replication early in the course of COVID-19.
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is an antimalarial/anti-inflammatory drug that impairs endosomal transfer of virions within human cells. HCQ is also a zinc ionophore that conveys zinc intracellularly to block the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase which is the core enzyme of the virus replication intracellularly to block the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase which is the core enzyme of the virus replication. Hydroxychloroquine was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1955, has been used by hundreds of millions of people worldwide since then, is sold over the counter in many countries. A typical HCQ regimen is 200 mg twice a day for 5 to 30 days depending on continued symptoms.
ANTIBODY THERAPY
Recently, Regeneron, a monoclonal antibody directed against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein has been approved for the early ambulatory treatment of COVID-19. If SARS-CoV-2 is diagnosed by rapid testing in a facility that performs antibody infusion such as an emergency room, urgent care center, or clinic, it is reasonable to start COVID-19 with the antibody infusion immediately. Conversely, if it can be safely arranged by home infusion while maintaining quarantine, physicians may prescribe this therapy to augment the effects of longer courses of oral treatment.
CYTOKINE STORM
The manifestations of COVID-19 that prompt hospitalization and that may well lead to multi-organ system failure are attributed to a cytokine storm. Some of the first respiratory findings are cough and difficulty breathing. These features are attributable to inflammation and cytokine activation. Early use of oral corticosteroids is a rational intervention for COVID-19 patients with these features as they would be in other inflammatory lung disorders
Dexamethasone 6 mg po qd or prednisone 1 mg/kg can be given orally per day for five days with or without a subsequent taper.
ASPIRIN
Given reports of catastrophic stroke and systemic thromboembolism and the large reductions in mortality for both prophylactic and therapeutic use, administration of aspirin 325 mg po qd for all COVID-19 patients and systemic anticoagulation is prudent in patients with a history of heart, lung, kidney, or malignant disease is prudent.





